Fixing the tech debt downside whereas staying aggressive and safe – Cyber Tech
CIOs face the difficult activity of balancing varied priorities to align their digital infrastructure with enterprise objectives. Waiting for the following 12-18 months, two prime priorities emerge for IT leaders: creating a robust enterprise case for AI infrastructure spending (cited by 35% of respondents to IDC’s Future Enterprise Resiliency and Spending Survey, Wave 3, March 2024) and rising cyber resilience and safety (34%). Apparently, regardless of the importance of technical debt as a price concern and an inhibitor to enhancing safety and implementing innovation (like AI), it ranks a lot decrease on the checklist of instant priorities for a lot of organizations (20%). This misalignment between priorities and actions creates a considerable barrier to success.
Future Enterprise Resiliency and Spending (FERS) Survey, Wave 3, IDC, March 2024
The overspending problem
The identical IDC survey knowledge reveals that 38% of IT professionals anticipate overspending on digital infrastructure this 12 months (larger than 20% will overspend between 1% and 9%, and 17% will overspend by 10% or extra). This overspending is primarily pushed by two components: extreme technical debt (cited by 47% of survey respondents) and an absence of business-aligned infrastructure technique (43%).
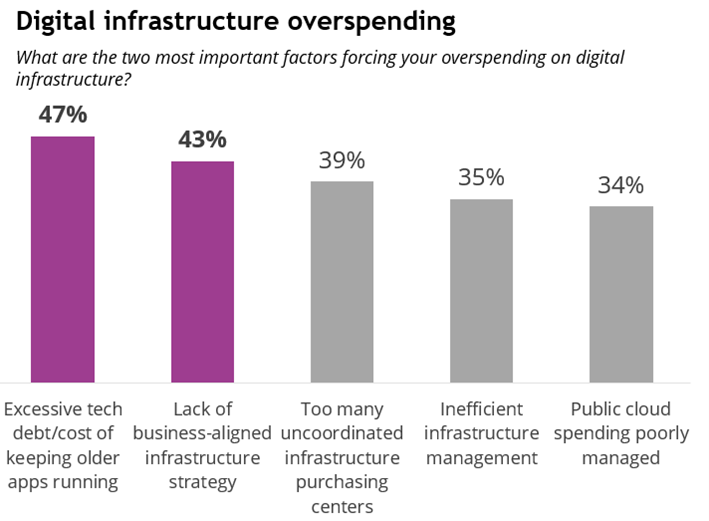
Future Enterprise Resiliency and Spending (FERS) Survey, Wave 3, IDC, March 2024
There appears to be a noticeable hole between the objectives CIOs set and the priorities they concentrate on to succeed in these objectives. Each AI and safety modernization require built-in programs and substantial budgets, but these components are inhibited by technical debt. As proven in IDC’s survey knowledge, whereas CIOs acknowledge that technical debt is a big barrier to key strategic initiatives, they usually don’t prioritize it as a foundational situation. It’s a standard situation amongst CIOs — it’s usually simpler to speak and acquire consensus with enterprise stakeholders on the pressing want for innovation (a competitiveness issue) and cybersecurity (an existential menace) than on addressing upkeep duties (technical debt).
Regardless of these challenges, CIOs can navigate the complexities by specializing in three key areas: balancing the administration of technical debt with future investments, constructing a robust enterprise case for AI, and enhancing cyber resilience and safety.
Growing a balanced technical debt strategy
Technical debt usually stems from the prices of operating and sustaining legacy know-how companies, particularly older purposes. It sometimes arises when organizations make short-term sacrifices or use fast fixes to deal with instant wants with out ever returning to resolve these momentary options.
For CIOs, balancing technical debt with different strategic priorities is a continuing problem. They need to resolve whether or not to take a position sources in high-profile areas like AI and safety or to prioritize lowering technical debt. Ignoring technical debt can result in escalating prices, inefficiency, and integration challenges, whereas deprioritizing it to concentrate on high-impact tasks (e.g., AI) might drive short-term enterprise worth on the expense of long-term drag. The secret’s to deal with essential areas of technical debt to step by step modernize the IT infrastructure wanted for innovation and safety. This strategy helps keep a steadiness between managing debt and driving innovation.
Capital One’s cloud migration initiative highlights a strategic strategy to managing technical debt. By migrating to the cloud and altering its know-how operations, Capital One was capable of scale to satisfy demand, enhance agility, speed up innovation, and cut back prices related to legacy programs. This instance reveals that whereas managing technical debt is essential, it may be balanced with different priorities.
Constructing a robust enterprise case for AI
AI is shortly turning into a key asset for organizations in search of to drive innovation, improve buyer expertise, and enhance operational effectivity. With the precise infrastructure, AI has the potential to rework enterprise operations and drive development. Growing a robust enterprise case for AI infrastructure is crucial for demonstrating its potential affect on enterprise outcomes, which suggests organizations might want to safe the required investments and assist for AI initiatives.
To make this occur, CIOs must articulate the tangible advantages and ROI of AI investments. They need to work intently with enterprise leaders to align AI tasks with enterprise objectives and make clear particular issues AI can remedy. This includes figuring out areas the place AI could make the most important distinction, comparable to customer support, provide chain administration, or predictive upkeep. IT groups can run pilot tasks to showcase AI’s capabilities and collect knowledge to assist broader implementation. These pilots ought to concentrate on clear, measurable outcomes to show success and construct confidence in AI options. As a part of these pilots, know-how leaders should assess how the manufacturing rollouts may be impacted by technical debt and triage the remediation.
One profitable instance of AI implementation is Netflix. Netflix makes use of AI algorithms to supply personalised suggestions to its customers. By analyzing viewing habits and preferences, AI helps Netflix recommend content material that customers usually tend to get pleasure from, enhancing the shopper expertise and driving consumer engagement. This AI-driven strategy has helped Netflix retain subscribers and enhance viewing time, contributing to the corporate’s development and aggressive edge.
Enhancing cyber resilience and safety
As cyber threats have gotten extra refined and unpredictable, they’ve uncovered important gaps in guaranteeing safety for enterprise operations. Having superior safety measures protects the group’s belongings and ensures compliance with regulatory necessities. CIOs ought to put money into sturdy cybersecurity measures, together with superior menace detection, response capabilities, and worker coaching. Sustaining software program updates and implementing multifactor authentication (MFA) and encryption will additional strengthen a corporation’s defenses.
Nonetheless, technical debt can considerably undermine these cybersecurity efforts. Legacy programs and outdated software program can have vulnerabilities ready to be exploited. Moreover, technical debt is commonly represented by a number of, disparate instruments acquired over time, which might hinder the implementation of a cohesive safety technique and enhance cybersecurity danger. Addressing technical debt is crucial for sustaining a robust safety posture and guaranteeing the long-term resilience of the group in opposition to refined cyberthreats.
After an information breach in 2013, Goal made substantial investments in cybersecurity. Hackers received into Goal’s community by means of third-party distributors, compromising credit score and debit card data for about 40 million clients. After the incident, Goal employed a brand new chief data safety officer (CISO) who centered on constructing superior cybersecurity capabilities that might develop alongside evolving threats to deal with a few of Goal’s vulnerabilities. The brand new CISO constructed a group of in-house consultants to embed these instruments into Goal’s web site and working programs to supply a seamless buyer expertise. Goal’s response illustrates the affect that investing in safety measures can have and highlights the significance of proactive safety investments.
Conclusion
With competing priorities and restricted sources accessible, CIOs are charged with allocating their budgets strategically and guaranteeing digital infrastructure investments align with their group’s overarching enterprise technique. AI and safety are prime priorities, however technical debt should even be addressed so IT infrastructure can stay environment friendly and able to supporting future development. The secret’s for CIOs to evaluate each short- and long-term objectives and discover a balanced strategy to managing technical debt whereas investing in innovation. CIOs ought to have a look at the way to body technical debt throughout the shadows of AI and cybersecurity to supply concrete causes to deal with technical debt.
Study extra about IDC’s analysis for know-how leaders.
Worldwide Information Company (IDC) is the premier world supplier of market intelligence, advisory companies, and occasions for the know-how markets. IDC is an entirely owned subsidiary of Worldwide Information Group (IDG Inc.), the world’s main tech media, knowledge, and advertising companies firm. Lately voted Analyst Agency of the 12 months for the third consecutive time, IDC’s Expertise Chief Options offer you professional steering backed by our industry-leading analysis and advisory companies, sturdy management and improvement packages, and best-in-class benchmarking and sourcing intelligence knowledge from the {industry}’s most skilled advisors. Contact us right now to study extra.
Mona Liddell is a analysis supervisor for IDC’s IT Government Applications (IEP). She is answerable for main the creation, evaluation, and supply of quantitative-based analysis and associated advertising content material for enterprise and know-how leaders. This analysis offers steering on the way to leverage know-how to attain progressive and disruptive enterprise outcomes. Mona has over 10 years of expertise utilizing knowledge to drive actionable insights and proposals. Previous to becoming a member of IDC, Mona served as a market insights advisor for the IBM infrastructure group. She led large-scale main analysis research and suggested the IBM Programs and IBM Cloud groups and govt management on technique, market dynamics and traits, and opponents.



